Boran Zhou (周博然)
boranzhou1313@gmail.com

I am currently a Research Associate at Mayo Clinic, where I conduct clinical research focus on interstitial lung disesase, carpal tunnel syndrome, penile dysfunction, glaucoma, unilateral papilledema, etc
Before Mayo Clinic, I was a research fellow at University of South Carolina, where I worked on vascular biomechanics using mechanical testing and numerical modeling.
I obtained my Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering at University of South Carolina, advised by Prof. Tarek Shazly. I obtained my bachelor degree from Harbin Institute of Technology, China.
I have a track record of creating and contributing to open source libraries.
My major interest is on the ultrasound elastography and vascular biomechanics.
I do have a LinkedIn profile.
Research
My current research topics include:
- Using ultrasound elastography for asessing elasticity of soft tissue.
- using deep learning to predict lung mass density.
- using convolutional neural network for medical image classfication.
(Most recent publications to be added)
Recent Publications
Links to: [Full List] [Google Scholar]
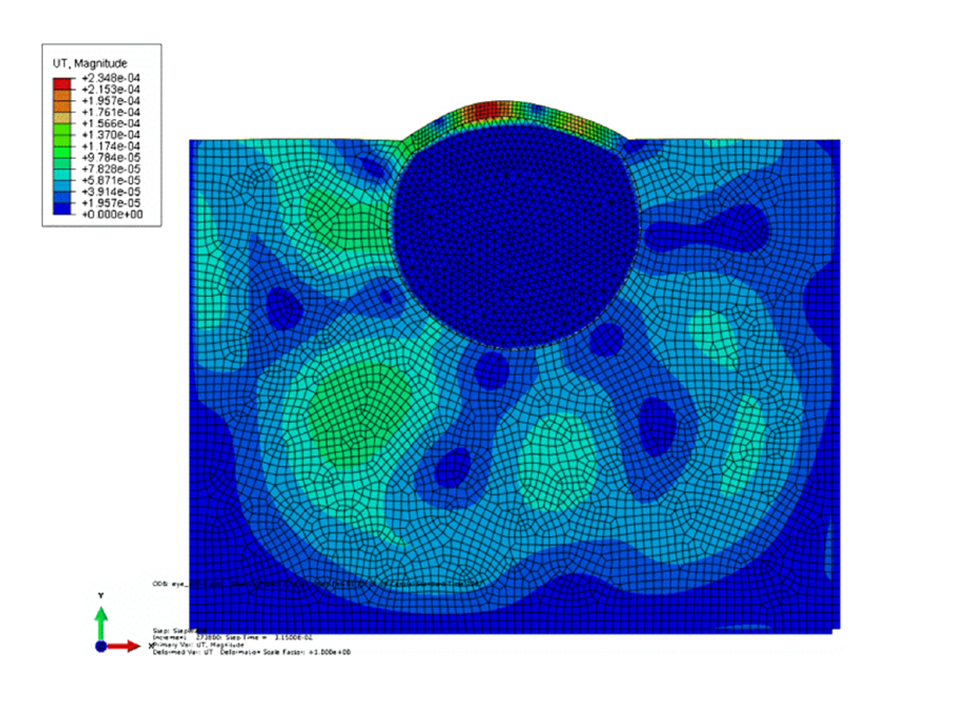
Noninvasive measurement of wave speed of porcine cornea in ex vivo porcine eyes for various intraocular pressures
Boran Zhou, Arthur J Sit, Xiaoming Zhang.
[PDF]
The objective of this study was to extend an ultrasound surface wave elastography (USWE) technique for noninvasive measurement of ocular tissue elastic properties. In particular, we aim to establish the relationship between the wave speed of cornea and the intraocular pressure (IOP).
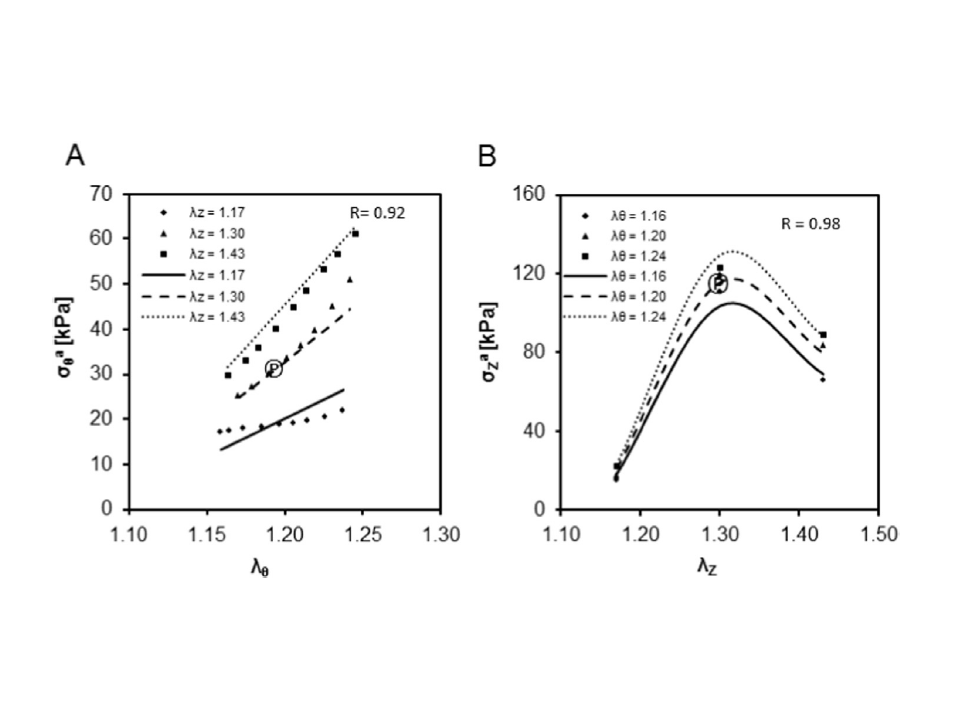
The biaxial active mechanical properties of the porcine primary renal artery
Boran Zhou, Alexander Rachev, Tarek Shazly.
[PDF]
This study is a continuation of our previous investigation, in which a four-fiber constitutive model of the passive response of the primary porcine renal artery was identified. Here we focus on the active response of this vessel, specifically in the case of maximal SMC contraction, and develop a constitutive model of the active stress–stretch relations.
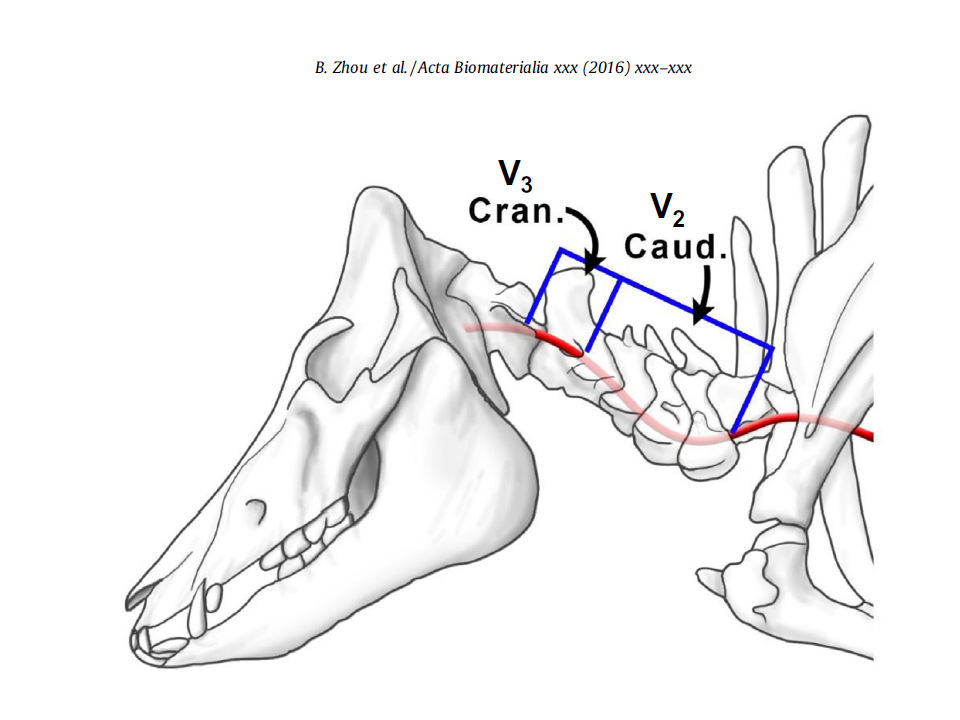
The perivascular environment along the vertebral artery governs segment-specific structural and mechanical properties
Boran Zhou, Mohammed Alshareef, David Prim, Michael Collins, Michael Kempner, Adam Hartstone-Rose, John F Eberth, Alexander Rachev, Tarek Shazly.
[PDF]
In this study, we compare the passive mechanical response of the central, juxtaposed arterial segments of porcine VAs (V2 and V3) via inflation-extension mechanical testing.
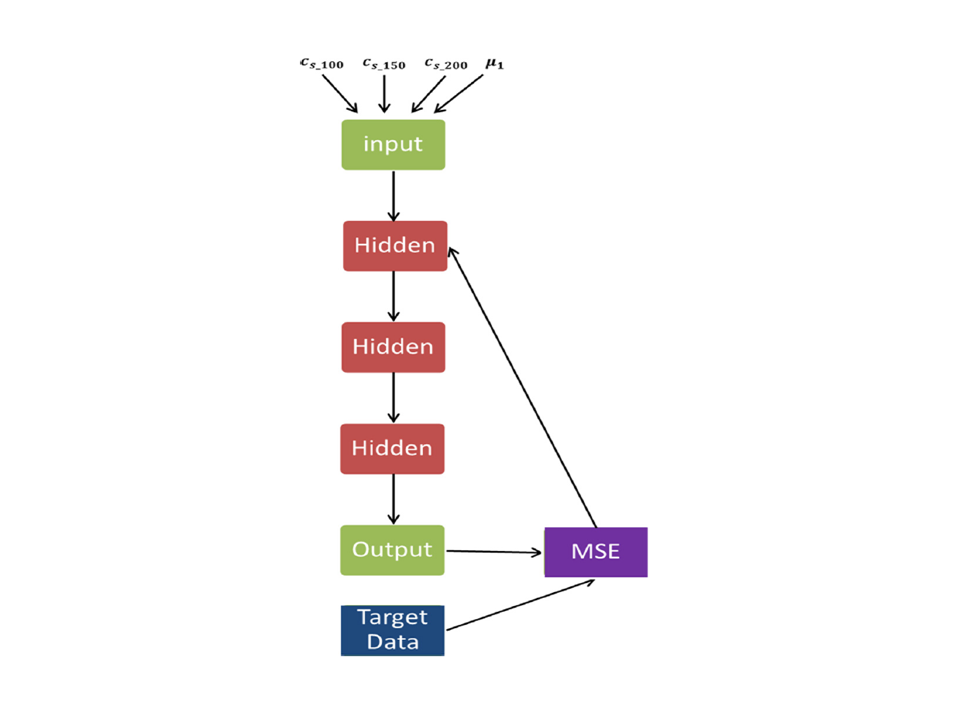
Lung mass density analysis using deep neural network and lung ultrasound surface wave elastography
Boran Zhou, Xiaoming Zhang.
[PDF]
We have developed a lung ultrasound surface wave elastography (LUSWE) technique to measure the surface wave speed of superficial lung tissue. The objective of this study was to develop a method for analyzing lung mass density of superficial lung tissue using a deep neural network (DNN) and synthetic data of wave speed measurements with LUSWE.
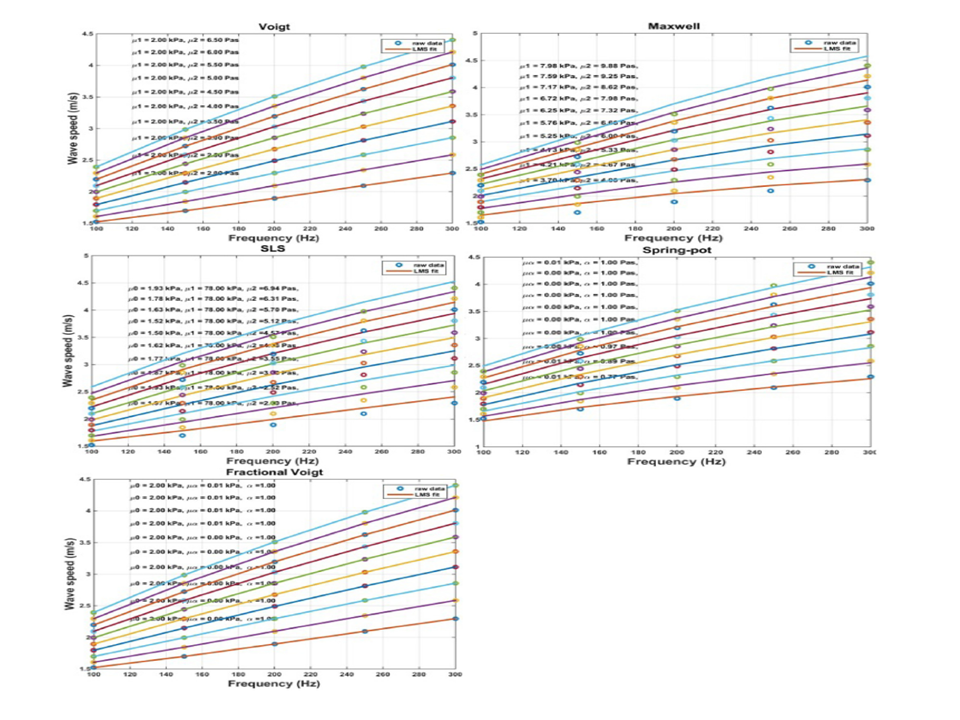
Comparison of five viscoelastic models for estimating viscoelastic parameters using ultrasound shear wave elastography
Boran Zhou, Xiaoming Zhang
[PDF]
The purpose of this study is to compare five viscoelastic models (Voigt, Maxwell, standard linear solid, spring-pot, and fractional Voigt models) for estimating viscoelastic properties based on ultrasound shear wave elastography measurements.
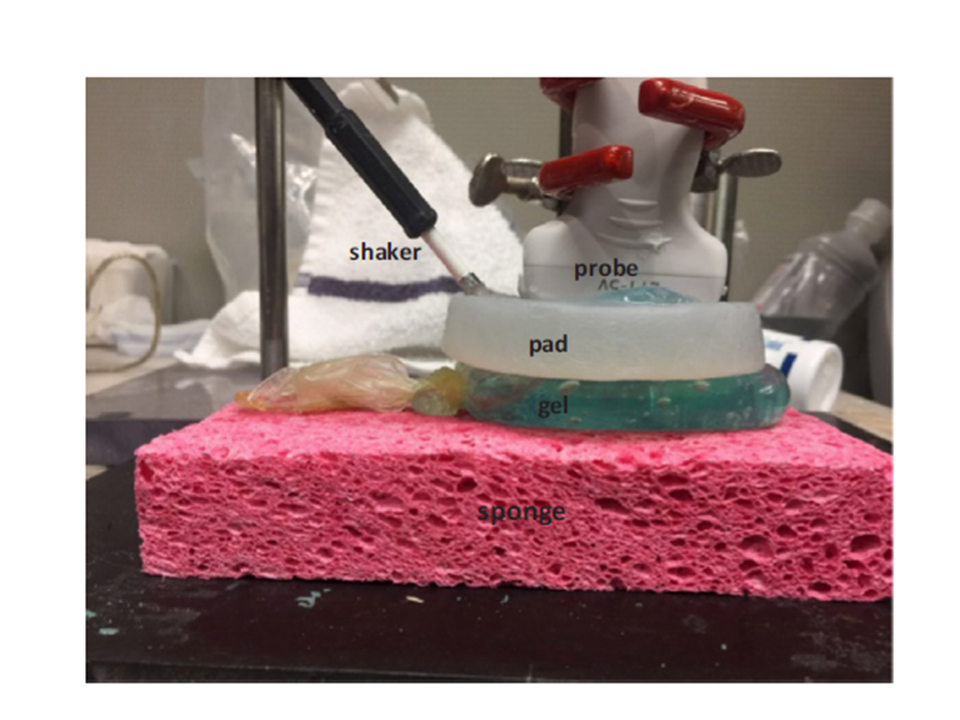
The effect of pleural fluid layers on lung surface wave speed measurement: Experimental and numerical studies on a sponge lung phantom
Boran Zhou, Xiaoming Zhang
[PDF]
By using lung ultrasound surface wave elastography (LUSWE) and finite element method (FEM), the effect of pleural effusion on the elasticity of superficial lung parenchyma in terms of surface wave speed measurement was evaluated in a sponge phantom study.